RAG Deep Dive Series: From Decision to Production
Part 1: The RAG Decision: When to Choose RAG Over Fine-Tuning
This is Part 1 of our RAG series, where we're breaking down Retrieval-Augmented Generation from first principles. We're starting from absolute zero if you've never heard terms like Embeddings, Vector Databases, or chunking, that's completely fine. We'll explain every concept as we encounter it, using analogies and examples that make the technical accessible.
Our goal? Give you the conceptual foundation to understand RAG deeply enough to make informed decisions about when to use it, how to architect it, and what tradeoffs you're making. We'll use analogies, diagrams, and real-world examples to explain the WHY and HOW behind each component not drown you in code or assume you already know the jargon.
Whether you're a product manager evaluating AI solutions, an engineer exploring RAG for the first time, or a technical leader trying to separate hype from reality, this series will give you the mental models you need. But before we dive into how RAG works, we need to start with a more fundamental question: *what problem does RAG solve?* And once we understand the problem, we can tackle the first decision every RAG project faces should you build with RAG at all, or is fine-tuning the better approach?
Let's start there.
Table of Contents
- The Problem: Why LLMs Alone Aren't Enough
- Two Paths Forward: Fine-Tuning vs. RAG
- The Verdict: A Real-World Decision
- Different Tools for Different Jobs
- What's Next in This Series
The Problem: Why LLMs Alone Aren't Enough
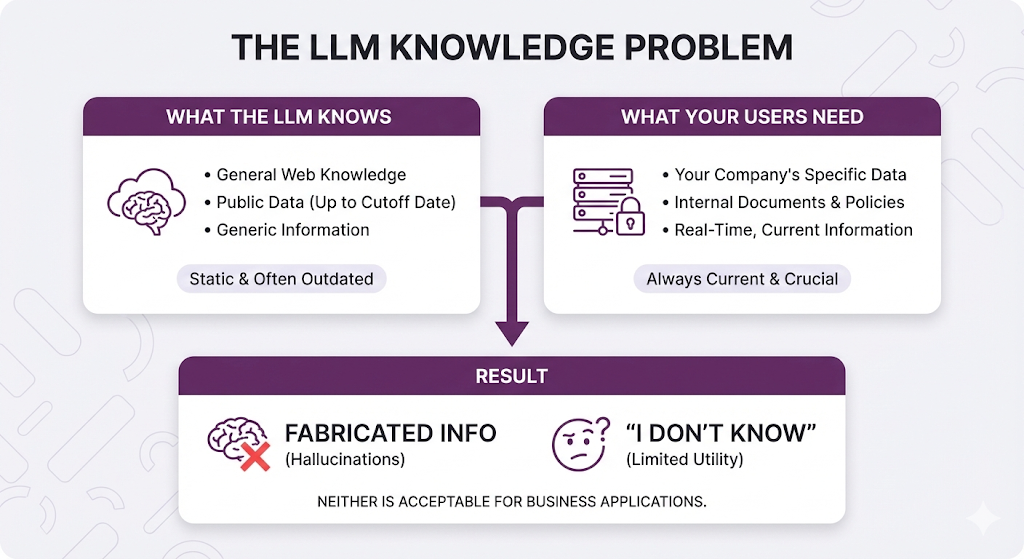
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini are incredibly powerful. They can write code, explain complex concepts, and have conversations that feel remarkably human. But here's the thing, they have some fundamental limitations that make them unreliable for enterprise and business-critical applications.
The Core Limitations of Standalone LLMs
- Knowledge Cutoff
LLMs are trained on data up to a certain date. After that? They're essentially frozen in time.
Example: Ask an LLM about your company's Q4 2024 sales figures, and it will either:
- Confidently make up numbers (hallucination)
- Admit it doesn't know
- Give you outdated information from its training data
This is a dealbreaker for any application that needs current, accurate information. - No Access to Private/Proprietary Data
Your company's HR policies, internal documentation, customer data, product manuals none of this exists in a public LLM's training data. The model literally has no idea about your specific business context.
There's a massive disconnect between what the LLM knows (general internet knowledge) and what your users need (specific, contextual answers about your data). - Hallucinations
This is the big one. LLMs don't "know" things they predict what text should come next based on patterns. When they don't have the right information, they'll generate plausible-sounding but completely fabricated answers.
Why This Matters:
- Legal implications if wrong advice is given
- Loss of user trust
- Potential business damage
In domains like healthcare, finance, or legal, a hallucinated answer isn't just wrong it's dangerous.
The Bottom Line
These three limitations create a perfect storm for enterprise applications:
So how do we fix this? There are two main approaches.
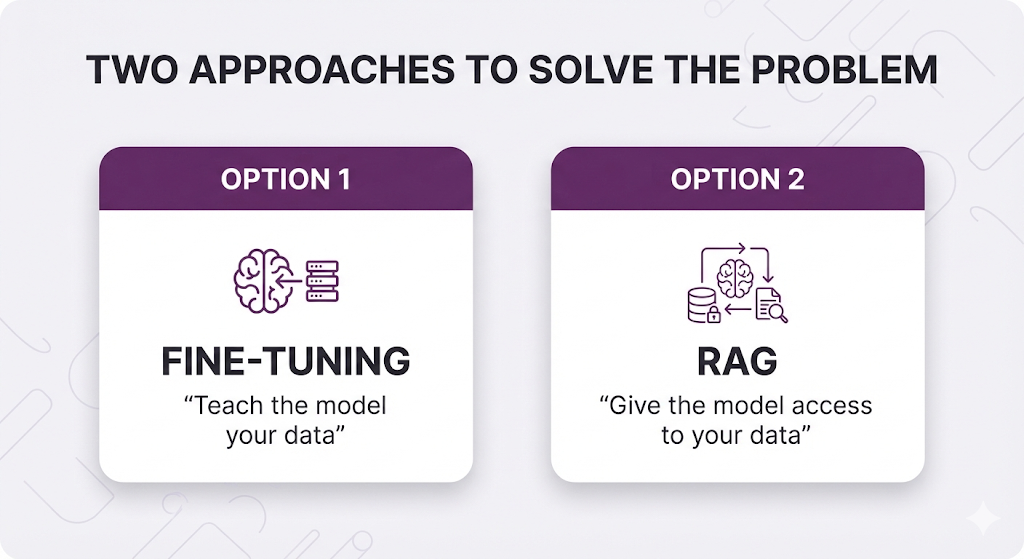
Two Paths Forward: Fine-Tuning vs. RAG
When faced with these LLM limitations, you have two primary options to inject domain-specific knowledge into your AI system:
Let's break down each approach.
Option 1: Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning is the process of taking a pre-trained LLM and training it further on your specific data. You're essentially "teaching" the model new information by updating its neural network weights.
How Fine-Tuning Works
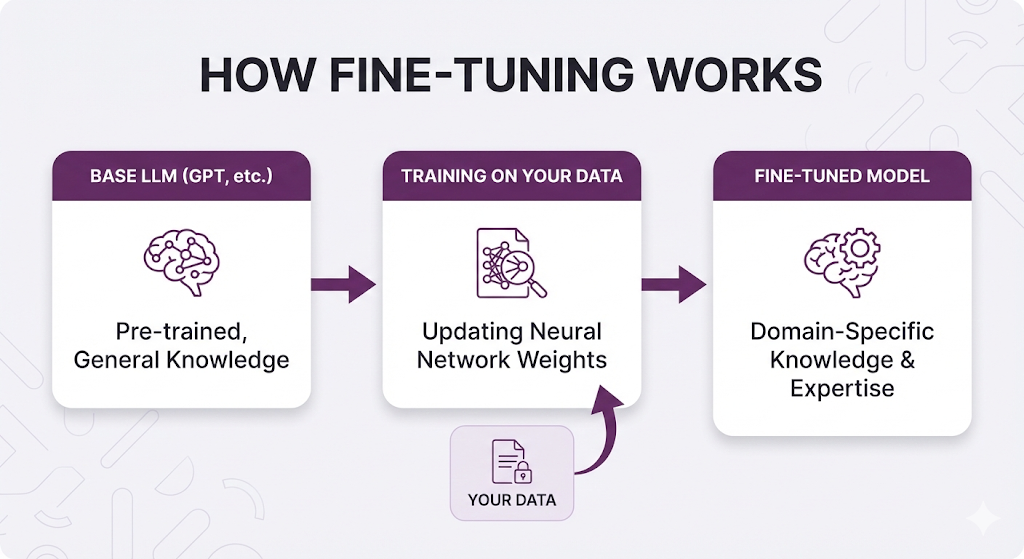
What Fine-Tuning Solves
| Problem | Does Fine-Tuning Help? |
|---|---|
| No access to private data | ✅ Yes - model learns your data |
| Hallucinations | ⚠️ Partially - better in trained domain |
| Knowledge cutoff | ❌ No - creates a NEW cutoff date |
The Limitations of Fine-Tuning
While fine-tuning sounds great in theory, it has significant drawbacks for knowledge-injection use cases:
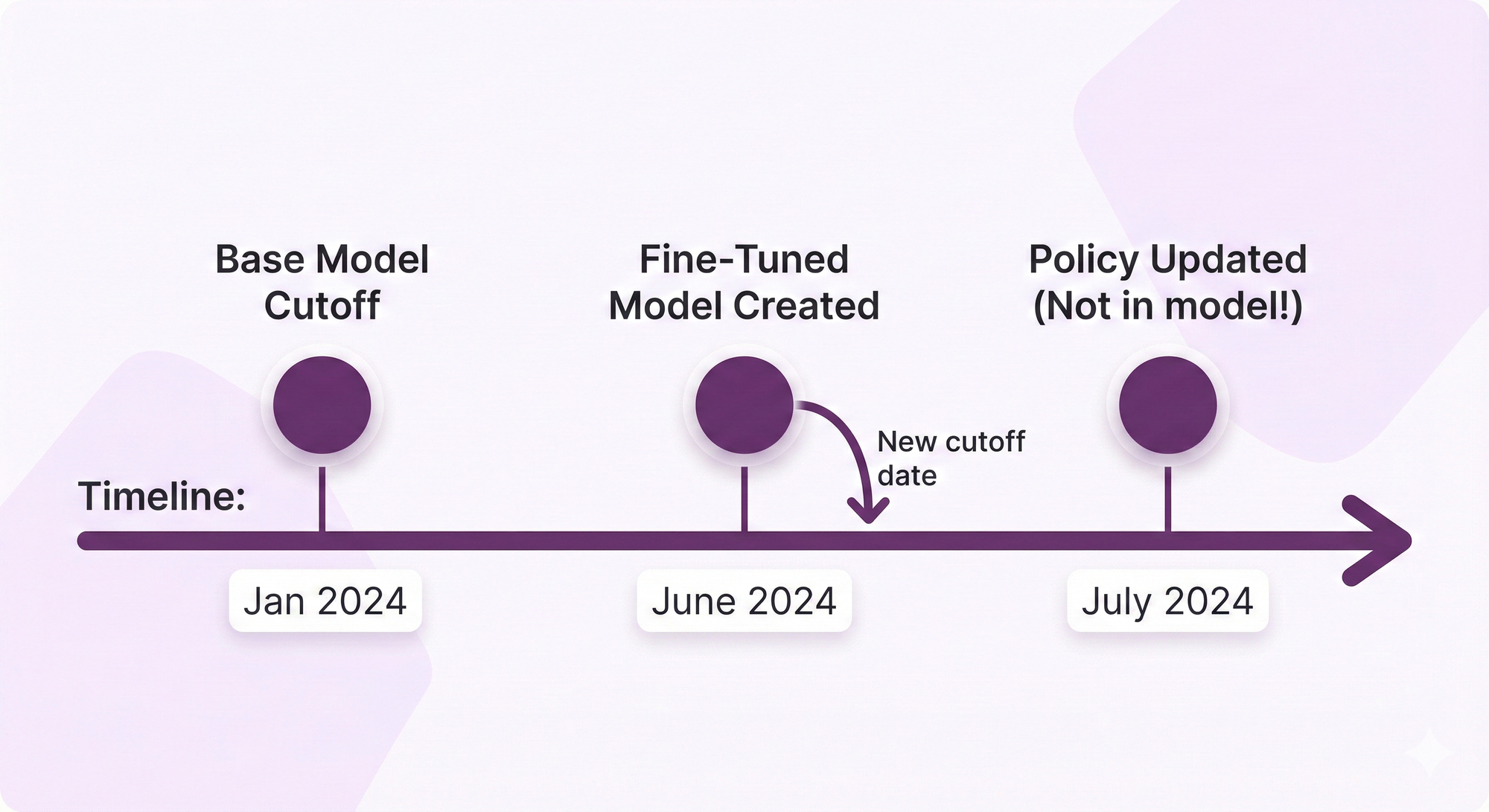
- Creates a New Knowledge Cutoff
Fine-tuning doesn't eliminate the knowledge cutoff problem it just moves it. Your fine-tuned model now knows data up to the date you trained it. Tomorrow's policy change? Not included.
- Requires Constant Retraining
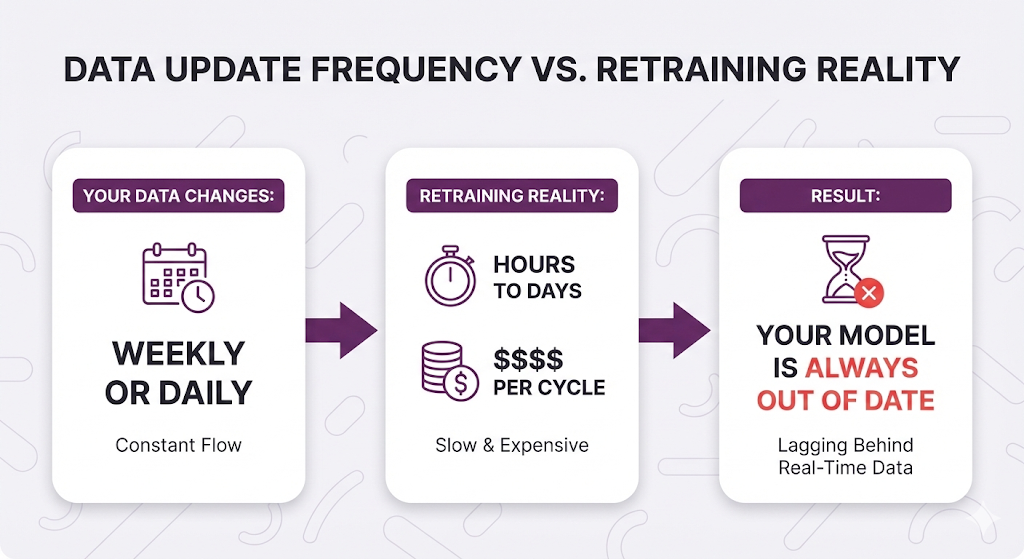
Every time your data changes, you need to retrain. For organizations with frequently updated information (policies, products, procedures), this creates a maintenance nightmare.
- High Cost & Resource Intensive
You're paying for GPU hours that add up fast, spending days on data prep (cleaning, formatting, quality checks the unglamorous stuff), and watching training cycles run for hours or even days at a time. Sure, modern fine-tuning APIs have made the basic process accessible to any developer, but getting it RIGHT, optimizing hyperparameters, preventing overfitting or diagnosing why accuracy dropped after retraining that's where the complexity lives. When things go wrong, debugging a fine-tuned model is significantly hard. - No Source Attribution
A fine-tuned model knows things, but it can't tell you WHERE it learned them. The knowledge is baked into billions of parameters there's no paper trail. - Risk of Catastrophic Forgetting
When you fine-tune on new data, the model can "forget" things it previously knew well. Balancing old and new knowledge is tricky. - Data privacy concern
Your proprietary data becomes part of the model weights. If you're using a cloud provider's fine-tuning service, your data leaves your control.
When Fine-Tuning DOES Make Sense
Fine-tuning isn't useless it's just not ideal for knowledge injection. And contrary to popular belief, you don't need fine-tuning for style, tone, or output format a well crafted system prompt handles those just fine.
So when IS fine-tuning actually worth it?
- Cost & Latency Optimization at Scale
If you're making millions of API calls, a fine-tuned model doesn't need lengthy system prompts repeated every time. Shorter prompts = fewer tokens = significant cost savings and faster responses. For real-time applications where every millisecond counts, this matters. - Domain-Specific Jargon & Terminology
When your domain has highly specialized language (medical codes, proprietary acronyms, niche technical terms) that the base model consistently misunderstands even with excellent prompts. - Model Distillation
Fine-tuning a smaller, cheaper model to behave like a larger one for your specific use case. For example, teaching GPT-4o-mini to respond like GPT-4o on your particular task getting premium quality at budget prices. - High-Volume Repetitive Tasks
For very specific, repetitive tasks (sentiment classification, entity extraction) where you need consistent, deterministic behavior millions of times without prompt overhead.
The Common Thread: Fine-tuning is about efficiency and consistency at scale, not about teaching knowledge or changing tone.
Option 2: RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
RAG takes a fundamentally different approach. Instead of teaching the model your data, you give it access to look up information when it needs it.
What is RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that solves the LLM knowledge problem by giving models access to external knowledge at inference time without retraining.
Think of RAG as giving your LLM a really smart research assistant. Instead of relying solely on what it memorized during training, the LLM can now:
- Search through your documents and data.
- Retrieve the most relevant information.
- Generate an answer grounded in that retrieved context
The Key Insight: Don't make the LLM memorize everything. Instead, give it the ability to look things up when it needs to.
Think of it like this: Fine-tuning is like studying for an exam you memorize everything beforehand, but you can't reference your notes during the test. RAG is like an open-book exam you don't memorize everything, but you know exactly where to find the answer when you need it.
How RAG Works (The 30-Second Version)
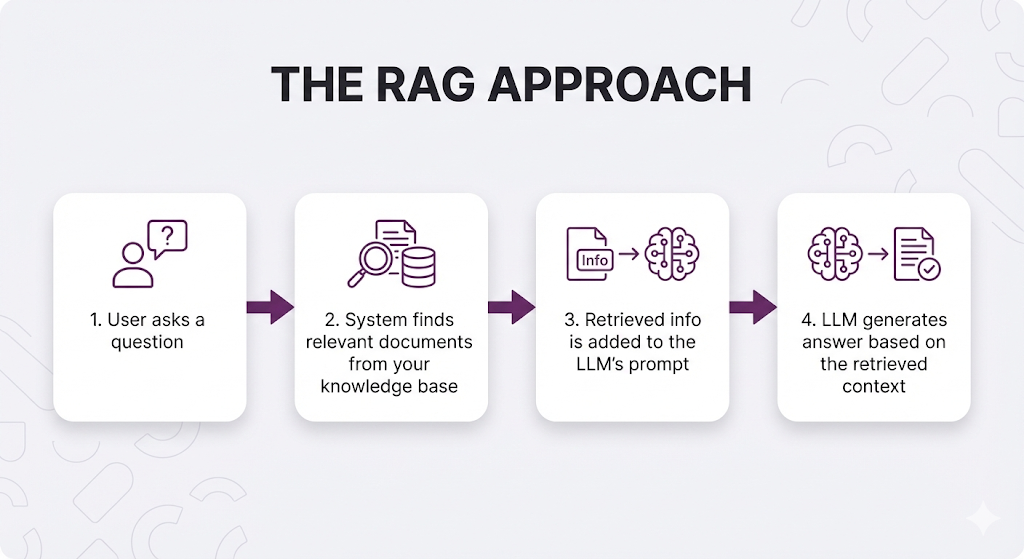
The LLM doesn't need to know your data. It just needs to receive the right context at query time.
What RAG Solves
| Problem | Does RAG Help? | How? |
|---|---|---|
| No access to private data | ✅ Yes | Data stays in your control, retrieved on-demand |
| Hallucinations | ✅ Yes | LLM answers from provided context, not memory |
| Knowledge cutoff | ✅ Yes | Update your docs = system is instantly updated |
| Source attribution | ✅ Yes | Every answer can cite its source |
| Cost at scale | ✅ Yes | No retraining costs, just retrieval |
| Data privacy | ✅ Yes | Your data never leaves your infrastructure |
The RAG Advantages
- Always Current
Update a policy document at 2 PM. By 2:01 PM, your RAG system knows about it. No retraining, no waiting, no deployment pipeline. - Source Attribution Built-In
Every answer can trace back to the exact document, section, and paragraph it came from. This is huge for:
- Compliance and auditing
- Building user trust
- Debugging wrong answers - Transparent & Debuggable
When RAG gives a wrong answer, you can see exactly what went wrong:
- Did it retrieve the wrong documents?
- Did the LLM misinterpret the context?
- Is the source document unclear?
With fine-tuning, debugging is a black box. - Cost-Effective Iteration
Want to improve your system?
- Reorganize your documents
- Improve your retrieval logic
- Add new data sources
- Test different LLMs - Hybrid Knowledge
RAG lets the LLM use BOTH its trained knowledge AND your specific data. Ask it to write a Python script using your company's API? It uses its coding knowledge + your API docs. Best of both worlds.
When RAG Makes Sense
RAG is the right choice when your data changes frequently think daily or weekly updates rather than static content. It's particularly valuable when you need source attribution for compliance, legal, or medical applications where every claim must be traceable. If you're working with diverse data sources like documents, wikis, emails, and databases that all need to be searchable in one place, RAG handles this naturally. The approach also shines when you need fast iteration cycles for rapid prototyping and A/B testing, since you can modify your knowledge base and retrieval logic without retraining. For organizations where data privacy is critical and information must stay within company infrastructure, RAG keeps everything under your control. Finally, if explainability matters if you need to debug wrong answers and continuously improve your system RAG's transparent retrieval process makes this straightforward in ways that fine-tuning simply can't match.
The Verdict: A Real-World Decision
Let's look at a concrete example to see how this decision plays out in practice.
Case Study: Customer Support Knowledge Base
A SaaS company with a portfolio of 100+ products wanted to help their support team quickly find accurate answers from product documentation, troubleshooting guides, and known issue databases.
The Requirements:
- Handle 50+ support agents searching across documentation for multiple products
- Provide accurate, cited answers to customer issues (wrong info = customer churn)
- Stay current with weekly product releases and feature updates
- Search across diverse content (product docs, troubleshooting guides, API references, known bugs)
- Fast iteration cycles to improve based on common support tickets
- Source attribution so agents can verify answers and share links with customers
The Decision Matrix
Here's how RAG and fine-tuning stacked up against these requirements:
| Requirement | Fine-Tuning | RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Handle weekly product updates | ❌ Retraining cycle every release | ✅ Update docs instantly |
| Search across multiple products | ⚠️ One model for all products | ✅ Multi-source retrieval built-in |
| Provide source citations | ❌ No attribution possible | ✅ Returns exact doc sections |
| Fast iteration | ❌ Days per training cycle | ✅ Test changes in minutes |
| Keep pace with feature velocity | ❌ Always lagging behind releases | ✅ Syncs with doc updates |
| Easier to debug/iterate | ⚠️ Complex when things break | ✅ Transparent, easier to fix |
| WINNER | — | RAG |
Why RAG Was the Clear Choice
The Update Velocity Problem:
The company ships new features weekly across their product portfolio. Product documentation, API references, and troubleshooting guides update constantly.
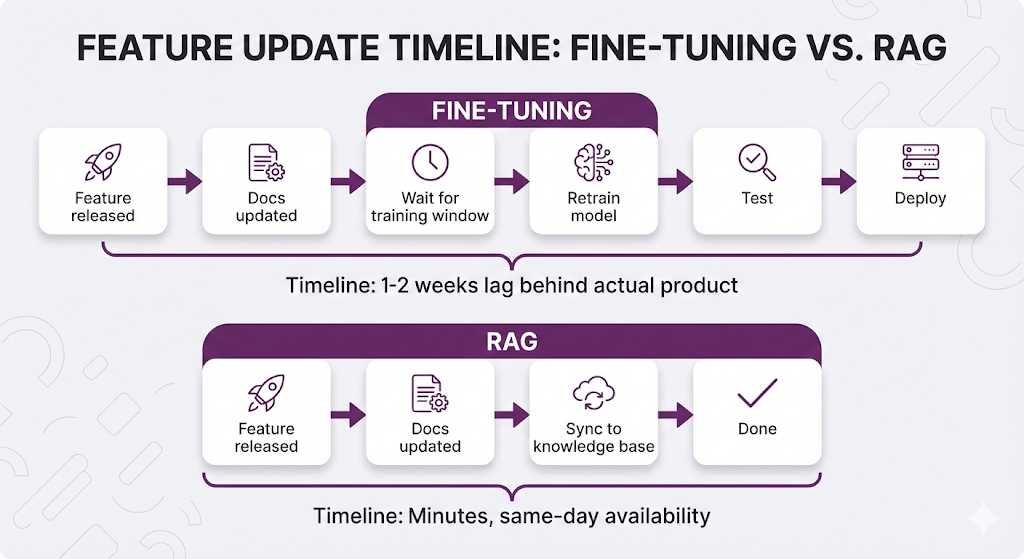
For a support team that needs answers about features released this morning, a 1-2 week lag is unacceptable.
The Multi-Source Problem:
Support agents need to search across:
- Product documentation (different docs per product)
- Troubleshooting guides (constantly updated with new issues)
- API references (versioned, multiple versions active)
- Known bugs database (changes daily)
- Internal runbooks (team-specific)
Fine-tuning would require:
- Retraining every time ANY source updates
- Managing knowledge conflicts between products
- No way to know which product/doc an answer came from
RAG handles this naturally each retrieved chunk includes its source, so agents know exactly where the information came from and can link customers directly to the relevant documentation.
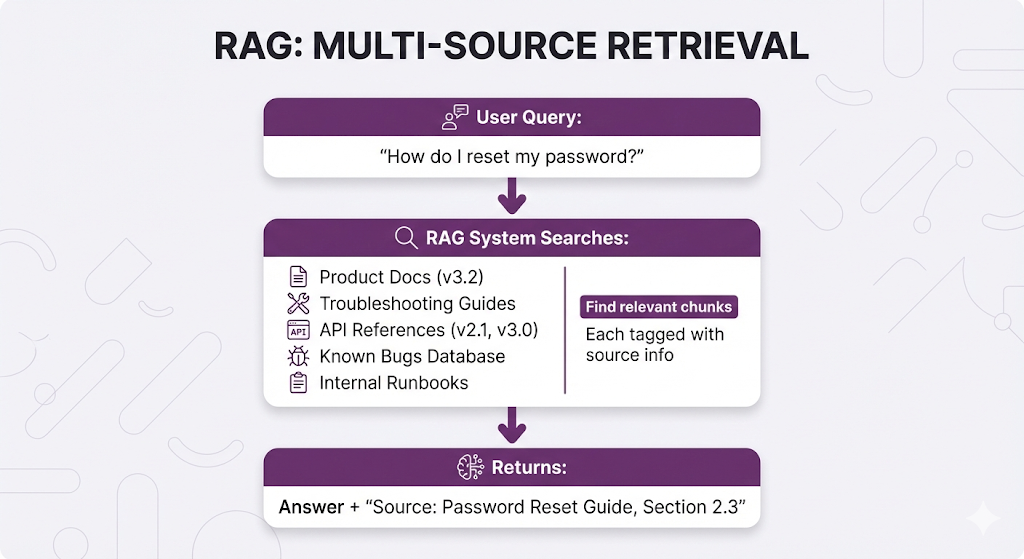
The Trust & Verification Problem:
When a support agent tells a customer "here's how to fix that," they need:
- Confidence the answer is current (not from 3 versions ago)
- A link to official documentation to share with the customer
- Ability to verify the answer themselves before responding
RAG provides all three. Fine-tuning provides none.
The Practical Result:
The company built their RAG system with these outcomes:
- ~92% accuracy on support query evaluation set
- Same-day availability for newly released features
- Source attribution for every answer (agents can link customers to docs)
- Multi-product search without model confusion
- Maintainable by existing team without hiring ML specialists
Could they have achieved this with fine-tuning? The technical answer is maybe but the practical answer is not sustainably. With 100+ products shipping features weekly, the retraining cadence alone would be untenable. They'd always be answering yesterday's questions with last week's knowledge.
Should You Choose RAG?
If you're evaluating RAG vs. fine-tuning for your use case, ask yourself these five questions:
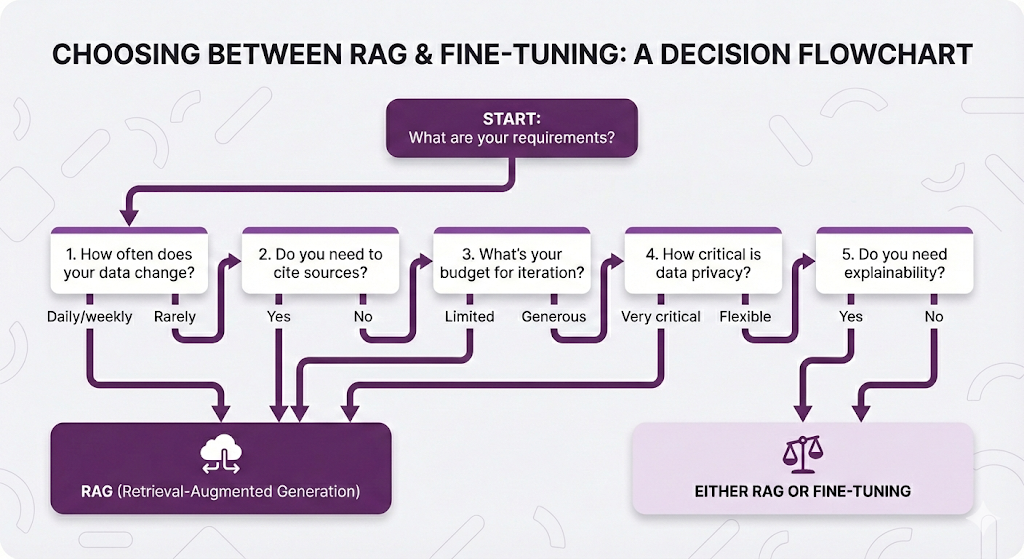
If you answered "RAG" to 3+ questions, you know where to start.
Bonus consideration: Even though modern fine-tuning APIs have lowered the barrier to entry, RAG remains more forgiving when things go wrong. Debugging why your RAG system retrieved the wrong documents is significantly easier than diagnosing why your fine-tuned model's accuracy dropped after retraining. For teams that need to move fast and iterate based on real-world feedback, RAG's transparency is a major advantage.
Different Tools for Different Jobs
Now that we've explored both approaches, here's a quick reference guide for when to use what:
Use FINE-TUNING when you need:
- Cost optimization at massive scale (millions of calls)
- Latency reduction (real-time applications)
- Domain-specific jargon the model keeps getting wrong
- Model distillation (small model mimics large one)
- Deterministic behavior on edge cases
Use RAG when you need:
- Company-specific or private information
- Frequently updated data (policies, products, docs)
- Source-cited, verifiable responses
- Current/real-time information
- Transparency and auditability
Pro Tip: These aren't mutually exclusive! You can use a fine-tuned model as your RAG generator for maximum efficiency combining RAG's knowledge access with fine-tuning's cost and latency benefits.
For most enterprise knowledge applications, RAG is the clear winner. But we've kept the explanation of how RAG actually works intentionally light in this post. In the next post, we'll break down the architecture, the 5 core components, and the two-phase operation that makes RAG tick.
What's Next in This Series
Here's the thing about RAG the concept is simple, but the implementation has layers.
Building a basic RAG system that works? You can do that in an afternoon. But building a RAG system that's production-ready, accurate, and fast? That's where understanding the fundamentals matters.
This series is designed to give you that deep understanding not through code tutorials, but through clear explanations of how each piece works and why it matters. Think of it as building your mental model of RAG from the ground up.
Roadmap
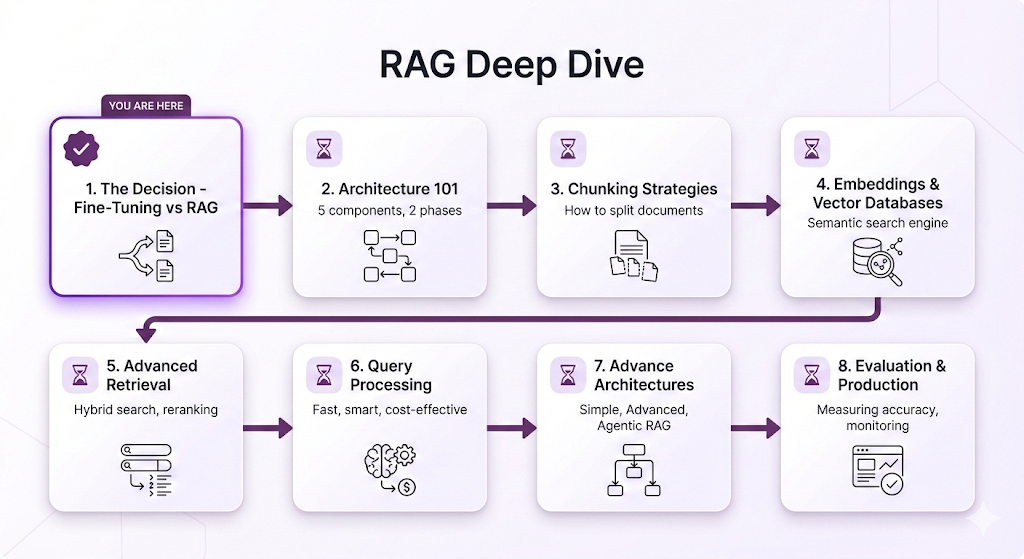
Each post builds on the last. We start with the big picture, then zoom into each component, and finally bring it all together for production deployment.
By the end, you'll understand:
- How RAG systems work conceptually (no code required)
- Which architectural decisions matter and why
- How to evaluate different approaches for your use case
- Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
See You in Post 2
So now you know WHY RAG wins for knowledge-intensive systems. But we've intentionally kept the HOW at a high level this post was about making the right decision, not building the system.
In the next post, we'll finally answer: How does RAG actually work?
You'll learn the 5 core components, the two-phase architecture, and get a complete walkthrough from question to answer. We're going from decision framework to architectural foundation.
Ready to Build Your RAG System?
We help companies build production-grade RAG systems that actually deliver results. Whether you're starting from scratch or optimizing an existing implementation, we bring the expertise to get you from concept to deployment. Contact us and Let's talk about your use case.

Part 1 of the RAG Deep Dive Series Next up: RAG Architecture 101

